What is Chain Printer? A Complete Guide for Students & Beginners
Published: 30 Apr 2025
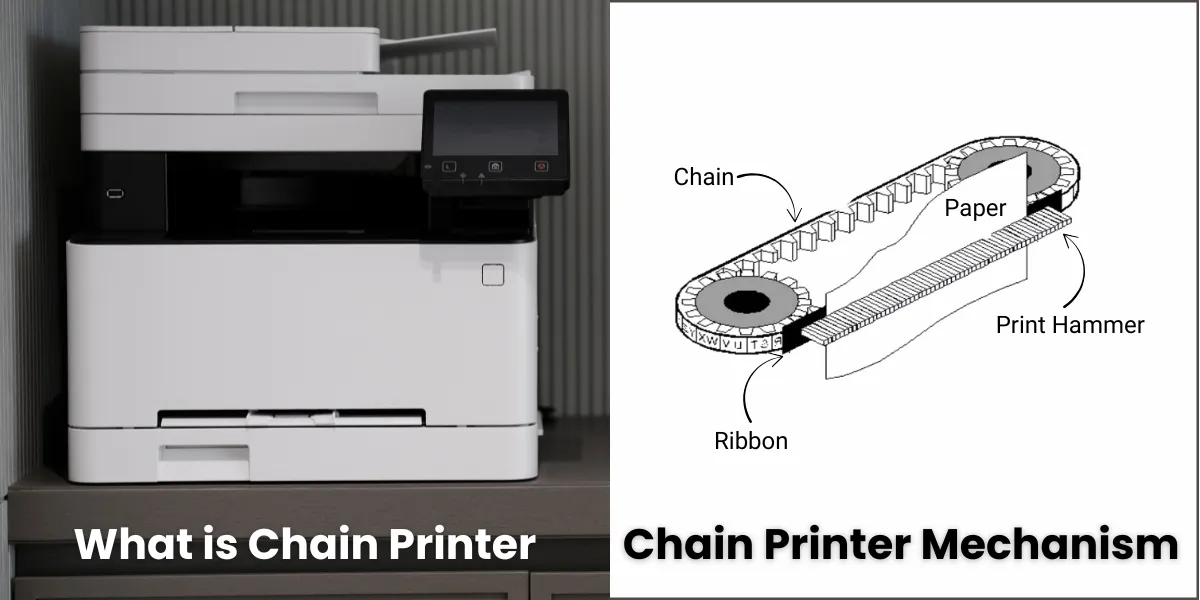
A chain printer is a type of line printer that can print hundreds of lines per minute using a rotating chain of characters.
In fact, some chain printers could print up to 1200 lines per minute, making them ideal for high-volume tasks in the 1970s and 80s.
Knowing what is chain printer helps us appreciate the evolution of printing technology and how early systems handled bulk data printing.
What is Chain Printer? (Explained Simply)
A chain printer is an old type of high-speed printer that prints one line at a time using a rotating metal chain. The chain has characters (like A to Z, 0 to 9) marked on it, and these characters hit an ink ribbon to print on paper.
You can imagine it like this:
It works kind of like nameplates on a moving chain. As the chain moves, a hammer hits the correct letter at the right time to print it on the page.
How is it different from modern printers?
- Chain printers use mechanical parts, while modern printers use ink or lasers.
- They were very fast, printing hundreds of lines per minute.
- But they were also noisy, bulky, and only printed in text (not images or color).
- Modern printers are quieter, smaller, and more flexible.
These printers were commonly used in banks, railways, and data centers during the 1970s–1990s, before laser and inkjet printers took over.
How Does a Chain Printer Work?
A chain printer works just like a moving bicycle chain. It prints an entire line at once by hitting paper through a ribbon. This type of printer was mainly used for fast, bulk printing in the past.
Let’s understand its working in simple steps:
Step-by-Step Working of Chain Printer:
- The chain moves across the page – A metal chain with characters keeps rotating horizontally in front of the paper.
- Hammers wait behind the paper – These small hammers are placed exactly behind each printing position.
- Right character comes in front – When the correct letter on the chain aligns with the hammer, it’s time to print.
- Hammer hits through ribbon – The hammer strikes, pressing the ribbon onto the paper and creating the printed letter.
Key Parts of a Chain Printer
A chain printer works using a few important mechanical parts. Let’s look at each component in simple words:

1. Chain or Print Chain or Metal Chain
The chain is a metal loop with characters (A to Z, 0 to 9) printed on it. It rotates continuously, and characters on the chain are used to print on paper.
2. Hammers
Hammers are small mechanical arms placed behind the paper. When the correct letter on the chain passes by, the hammer hits it forward through the ribbon to make an imprint.
3. Ribbon (Ink)
The ribbon holds the ink. When the hammer hits a character, it pushes the ribbon against the paper — that’s how the letter gets printed.
4. Paper Feed
This part moves the paper up, line by line, after each print so the next line can be printed clearly.
5. Control Unit
The control unit works like the brain. It decides which character to print, when to move the paper, and when to stop or start the chain.
6. Printer Head (Fixed Type)
Unlike inkjet printers, the print head in a chain printer stays in place. It aligns the hammers and characters for perfect printing.
7. Drive Motor
This motor powers the movement of the chain and paper feed. It keeps everything running smoothly at high speed.
8. Other Small Parts
- Sensors: Help detect timing and hammer positions
- Frame: The outer body that holds all parts
- Cooling Fans: Prevents printer from overheating
- Switches and Buttons: Control functions of chain printer
- Gear wheels: (help in chain movement)
All these parts work together smoothly to print fast and clear lines, one after another.
Uses of Chain Printer
Chain printers were very popular before laser and inkjet printers became common. They were used in places where fast and continuous printing was needed.
Here are the top uses of chain printers:
- Banks – For printing large daily transaction records
- Railway stations – For printing passenger reservation charts
- Government offices – For printing reports and forms in bulk
- Factories – Used in mainframes to print logs and inventory reports
- Stock exchanges – For printing stock price updates and lists
- Insurance companies – To print claim reports and client records
- Billing systems – For printing utility bills like electricity and water
- Schools & colleges – To print exam results and admission lists
- Data centers – Where huge amounts of data needed to be printed daily
- Hospitals – For printing patient admission/discharge records
- Warehouses – For bulk printing of packing lists and delivery slips
These printers were preferred because they could print fast and non-stop, especially when thousands of pages had to be printed quickly.
Real-Life Examples of Chain Printers
Chain printers played a big role in many offices during the early days of computers. They were strong, fast, and built for heavy-duty printing tasks.
Here are some real-life examples of how they were used:
- Banks: Used chain printers to print long customer account statements every day.
- Airlines: Printed boarding passes and flight tickets quickly before computers became advanced.
- Data Centers: Printed thousands of reports and logs daily using large mainframe systems.
- Railways: Used them to prepare printed reservation charts and timetables.
- Utility Companies: Sent monthly electricity and water bills to thousands of homes using these printers.
- Government Offices: Printed official records, notices, and forms in bulk.
- Hospitals: Used to print patient details, test reports, and shift schedules for staff.
“It was the backbone of early computer printing — trusted for speed and strength.”
Even though they are rarely seen today, chain printers helped shape the way we managed bulk data printing in the past.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Chain Printers
Let’s explore both the good and the not-so-good sides of chain printers in simple words. This will help you understand when they were useful and why they were replaced later.
| Advantages of Chain Printers: |
|---|
|
Chain printers were popular because they offered some impressive benefits during their time. Here are the main advantages:
That’s why chain printers were the go-to choice for big organizations that needed reliable and fast printing every day. |
| Disadvantages of Chain Printers |
|---|
|
Even though chain printers were useful, they also had some drawbacks. Here are the main reasons why they are not used today:
While chain printers were once powerful tools, their drawbacks led to the rise of modern, quiet, and feature-rich printers. |
Chain Printer vs Dot Matrix Printer (Comparison Table)
Both chain printers and dot matrix printers were popular in earlier days, but they worked differently. Let me explain it in a simple way so you can clearly see the difference.
Here’s a side-by-side comparison:
Feature | Chain Printer | Dot Matrix Printer |
Speed | Very High (up to 2000 lines/min) | Moderate (around 300–600 characters/sec) |
Noise | Very Noisy | Moderate Noise |
Flexibility | Low – fixed characters only | High – can print graphics and various fonts |
Print Quality | Good for text, not images | Lower resolution but versatile |
Cost | Expensive (industrial use) | More Affordable (home/school use) |
Size | Bulky and heavy | Compact and lighter |
Best Use | Banks, railways, data centers | Schools, offices, receipts |
In simple words: If speed was the main goal, chain printers won. But for flexibility and lower cost, dot matrix printers became more popular.
Why Chain Printers Are Rare Today
Chain printers were once the kings of speed. But like every old technology, they slowly faded away. Today, you rarely see them — even in big offices or banks.
Modern printers like laser and inkjet took over because they are:
- Quieter
- Smaller
- Cheaper
- Easier to use
- Capable of printing graphics and color
These features made modern printers a better choice for homes, schools, and businesses.
💔Like old telephones with rotary dials, chain printers are now history. But they played a big role in the early computer world.
Today’s printers are built for flexibility and style — not just speed. And that’s why chain printers slowly disappeared from the scene.
Quick Summary / Key Takeaways
- Chain Printers were fast printers that used a moving chain to print characters onto paper.
- They were widely used in banks, data centers, and railways for printing bulk documents.
- Unlike modern printers, they used hammers and ribbons for each character, making them noisy but effective for large tasks.
- Advantages: Fast, durable, great for high-volume printing.
- Disadvantages: Noisy, heavy, limited fonts, and high cost.
- Modern laser and inkjet printers replaced chain printers due to better features, like quiet operation and color printing.
Conclusion
So now you know what is chain printer and how it played a big role in early computer history. It was a powerful line printer that made fast and clear printing possible when computers were still new. Even though it’s no longer used today, it was once the backbone of printing in banks, offices, and data centers.
As you continue your journey in learning about old technologies, remember—every device, no matter how old, helped build the digital world we enjoy today. Every classic machine has a story to tell. Isn’t that inspiring?
Found this helpful? Share it with your friends who love computer history!
Got any questions about what is chain printer? Ask in the comments — I personally reply and help out all readers!
FAQs About Chain Printers
Many students and beginners often have questions while learning about chain printers. Below, I’ve answered some of the most common ones in a simple and easy way.
Still curious or confused about anything? Just ask in the comment section—I’m here to help you!
A chain printer is an output device. It prints text or images onto paper by striking a ribbon with a moving chain of characters.
It’s called a chain printer because it uses a moving chain that carries the characters. These characters strike the paper to print the desired output.
Chain printers were widely used in businesses, banks, and data centers to print large volumes of text quickly. They were also common in airlines and railways for ticket printing.
Chain printers are rarely available today as they have been replaced by faster and more efficient printing technologies like laser and inkjet printers.
Dot matrix printers, laser printers, and inkjet printers replaced chain printers. These new technologies offer better quality, faster printing, and quieter operations.
Chain printers have almost disappeared in modern industries. However, some old warehouses or legacy systems might still use them for specific tasks that require bulk printing.
The main advantage of chain printers is their speed. They can print a large amount of text quickly, making them ideal for bulk printing tasks.
Yes, a chain printer is an impact printer. It works by physically striking the paper through an ink ribbon to create printed characters, just like a typewriter.
Yes, chain printers are quite noisy. The moving chain and hammers make loud sounds during the printing process, which is one of their main drawbacks.
A chain printer uses a rotating chain with characters, while a drum printer uses a cylindrical drum with characters engraved on it. Both are impact printers, but their printing mechanisms and speed differ.
Chain printers typically use continuous paper or fanfold paper. This type of paper allows uninterrupted printing over long periods.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks