Real-Life Examples of Embedded Computers in Modern Technology
Published: 7 Mar 2025
Welcome Guys
Did you know that 98% of all microprocessors manufactured today are used in embedded systems? From smartphones to cars, these tiny computers power our daily lives without us even realizing it.
Embedded computers are designed to perform specific tasks efficiently, making modern technology smarter and more automated.
In this post, we’ll explore real-life examples of embedded computers across different industries and how they impact the way we live and work.
What is an Embedded Computer?
An embedded computer is a small, specialized computer built into a device to perform a specific function based on its functional requirements.
Unlike regular general-purpose computers, which can run multiple programs, embedded computers are designed to do one job efficiently.
Key Characteristics of Embedded Computers:
- Dedicated Function – Designed for a single task, like controlling a microwave’s heating system.
- Part of a Larger System – Works inside a bigger device, such as a car’s braking system.
- Compact and Efficient – Small in size, consumes less power, and runs smoothly.
- Real-Time Processing – Quickly processes data to automate tasks, like adjusting your car’s speed.
Real-Life Example: Smartwatch
A smartwatch tracks your steps, heart rate, and sleep patterns without needing an external computer. Its embedded system processes the data instantly, helping you monitor your fitness in real time.
Without wasting time, let’s explore real-world examples of embedded systems in everyday applications.
Real-Life Examples of Embedded Computers
Embedded computers are everywhere, making our daily tasks easier. From home appliances to medical equipment, these systems enhance automation, efficiency, and safety across various industries. Let’s explore these real-life applications of embedded computers one by one.

Home and Personal Devices
Embedded computers make everyday appliances smarter, more efficient, and easier to use. These devices automate tasks, saving time and energy while improving convenience.
- Smart TVs – Stream content, adjust picture settings, and connect to the internet automatically.
- TV Remote Control – Sends infrared or Bluetooth signals to control TV functions wirelessly.
- Washing Machines – Detect load size, adjust water levels, and optimize washing cycles.
- Microwaves – Control cooking time, temperature, and power levels for even heating.
- Air Conditioners – Adjust temperature based on room conditions and user preferences.
- Smartwatches – Track fitness, heart rate, and notifications in real-time.
- Refrigerators – Maintain cooling, detect temperature changes, and prevent food spoilage.
- Dishwashers – Optimize water usage, heat drying, and cleaning cycles.
- Coffee Makers – Brew coffee at preset times with the perfect temperature control.
- Doorbell Cameras – Detect motion, record footage, and send alerts to smartphones.
- Smart Thermostats – Learn user habits and adjust temperatures to save energy.
- Electric Toothbrushes – Monitor brushing pressure, time, and technique for better dental care.
How They Work
- Use sensors to detect conditions like temperature, motion, or pressure.
- Process data and automate actions (e.g., adjusting cooling in a fridge).
- Improve efficiency by optimizing power, time, and performance.
Tip: Smart home devices save time and energy by automating daily tasks like temperature control, cleaning, and security monitoring, making life easier and more cost-effective.
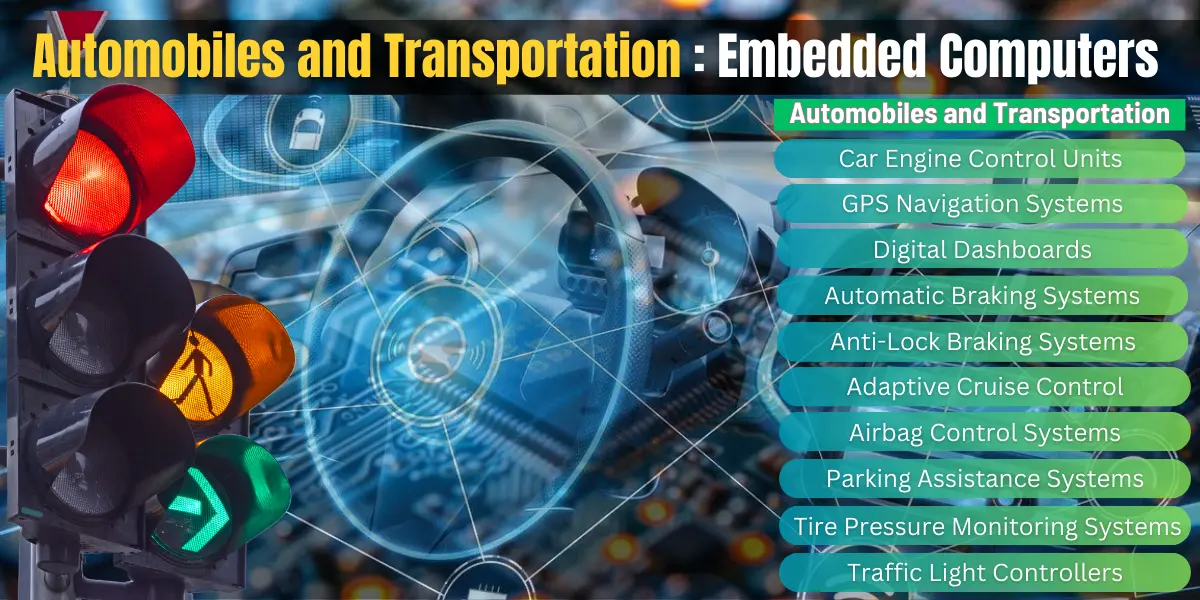
Automobiles and Transportation
Embedded computers play a crucial role in modern vehicles, improving safety, automation, and navigation. From managing fuel efficiency to assisting with parking, these systems make driving smarter and more reliable.
- Car Engine Control Units (ECU) – Adjust fuel injection, air intake, and ignition timing for better performance.
- GPS Navigation Systems – Calculate the fastest route, track real-time location, and provide voice directions.
- Digital Dashboards – Display speed, fuel level, and warnings with integrated smart controls.
- Automatic Braking Systems – Detect obstacles and apply brakes automatically to prevent collisions.
- Anti-Lock Braking Systems (ABS) – Prevent wheels from locking up during sudden braking, improving control and reducing skidding.
- Adaptive Cruise Control – Maintain a safe distance by adjusting speed based on traffic conditions.
- Airbag Control Systems – Monitor impact force and deploy airbags instantly for passenger safety.
- Parking Assistance Systems – Use sensors and cameras to guide drivers in parallel and reverse parking.
- Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems – Detect low air pressure and alert drivers to prevent tire damage.
- Electric Vehicle Charging Stations – Regulate power flow and optimize battery charging efficiency.
- Traffic Light Controllers – Adjust signal timing using sensors to improve traffic flow and reduce congestion.
How They Work
- Use sensors to monitor speed, pressure, and surroundings for real-time decision-making.
- Process data and automate driving functions like braking, acceleration, and navigation.
- Improve efficiency by optimizing fuel consumption, battery usage, and safety mechanisms.
Tip: ECUs control fuel efficiency by adjusting fuel injection, air intake, and ignition timing, reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
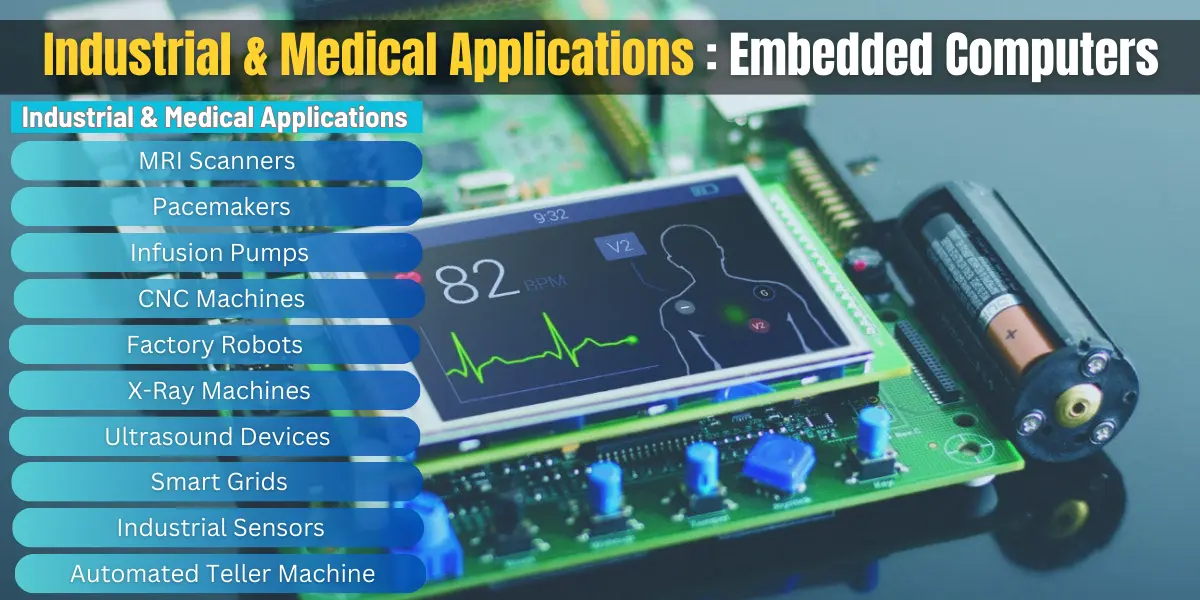
Industrial and Medical Applications
Real-time embedded systems play a crucial role in industrial automation, banking services like automated teller machines (ATMs), and life-saving medical equipment. These systems ensure precision, efficiency, and safety in manufacturing, energy management, and healthcare.
- Factory Robots – Perform automated assembly, welding, and material handling with high precision.
- CNC Machines – Control cutting, drilling, and shaping processes for accurate manufacturing.
- MRI Scanners – Process magnetic signals to generate detailed images of internal body structures.
- Pacemakers – Regulate heartbeats using electrical pulses to prevent cardiac irregularities.
- Infusion Pumps – Deliver precise doses of medication or fluids to patients automatically.
- X-Ray Machines – Use radiation to capture images of bones and tissues for medical diagnosis.
- Ultrasound Devices – Emit sound waves to create real-time images of organs and pregnancies.
- Smart Grids – Monitor and control electricity distribution for efficient energy use.
- Industrial Sensors – Track temperature, pressure, and vibrations to ensure machine safety.
- Automated Warehousing Systems – Manage inventory, transport goods, and optimize storage operations.
- Automated Teller Machine (ATM) – Processes banking transactions securely without human assistance.
How They Work
- Use sensors, hardware components and real-time data processing for accuracy and automation.
- Control complex operations with minimal human intervention, improving efficiency.
- Enhance safety by monitoring systems, detecting faults, and preventing failures.
Tip: Embedded computers save lives by powering devices like pacemakers, which continuously monitor and regulate heart rhythms, preventing cardiac emergencies.

Consumer Electronics and Smart Devices
Embedded computing system make digital devices smarter, faster, and more interactive. From smartphones to gaming consoles, they enhance user experience with AI, connectivity, and real-time processing.
- Smartphones – Power communication, apps, cameras, and internet browsing seamlessly.
- Digital Cameras – Process images instantly, adjust settings, and store high-quality photos.
- Gaming Consoles – Render real-time graphics, process player inputs, and enhance gaming performance.
- Smart Speakers – Recognize voice commands, play music, and control smart home devices.
- E-Readers – Optimize screen brightness and store thousands of books for easy reading.
- VR Headsets – Track movement, process 3D visuals, and create immersive virtual experiences.
- Wireless Earbuds – Use Bluetooth for seamless audio streaming and noise cancellation.
- Smart Light Bulbs – Adjust brightness, color, and schedules using remote or voice control.
- Smart Locks – Allow keyless entry using fingerprints, passwords, or smartphone apps.
- Fitness Trackers – Monitor heart rate, steps, and sleep patterns to improve health.
How They Work
- Process user inputs and deliver instant responses for a seamless experience.
- Use AI and sensors to track activities, recognize voices, and optimize performance.
- Enhance connectivity by integrating with apps, cloud services, and smart ecosystems.
Tip: Gaming consoles rely on embedded systems for real-time graphics rendering, ensuring smooth gameplay without lag.

Security and Defense Systems
Embedded computers play a critical role in security systems and defense, ensuring real-time monitoring, threat detection, and secure access control. These systems help protect people, data, and assets with advanced automation and precision.
- Surveillance Cameras – Capture, store, and analyze video footage for security monitoring.
- Drones – Perform aerial surveillance, reconnaissance, and security patrols.
- Radar Systems – Detect objects, monitor movement, and assist in navigation.
- Biometric Scanners – Authenticate identities using fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans.
- Motion Detectors – Sense movement and trigger alarms or security responses.
- Fire Alarm Systems – Detect smoke, heat, or gas leaks and activate emergency alerts.
- Access Control Systems – Restrict entry to authorized personnel using keycards or biometrics.
- Military Drones – Conduct surveillance, reconnaissance, and tactical operations.
- Anti-Theft Systems – Use sensors and alarms to prevent unauthorized access to valuables.
- Electronic Voting Machines (EVM) – Ensure secure and tamper-proof electronic elections.
How They Work
- Process real-time data from sensors and cameras for instant threat detection.
- Automate security responses, such as triggering alarms or alerting authorities.
- Enhance protection by using encryption, biometric authentication, and AI-based monitoring.
Tip: Biometric scanners use embedded computers to analyze unique physical traits like fingerprints or facial features, ensuring secure and accurate identity authentication.
So, guys, we’re wrapping up the section on real-life examples of embedded computers. Now, let’s move on to the next section about how embedded computers are transforming tomorrow.
How Embedded Computers Shape the Future
Embedded computing systems are evolving rapidly, driving innovations in AI, IoT, and automation. As technology advances, these systems will make devices smarter, more connected, and highly autonomous.
- The Rise of AI-Powered Embedded Systems – AI integration enables real-time decision-making, automation, and personalized user experiences.
- 5G and IoT Integration for Smarter Devices – Faster connectivity will allow seamless communication between smart devices, improving efficiency and automation.
- How Autonomous Vehicles Will Rely on Embedded Computers – Self-driving cars will use embedded systems for real-time navigation, obstacle detection, and decision-making.
The Future of Embedded Computers
- AI-driven automation will enhance industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and security.
- Faster networks (5G) will boost IoT capabilities, making smart homes and cities more efficient.
- Autonomous systems will reduce human intervention, leading to safer and smarter operations.
Tip: AI-powered embedded computers will revolutionize everyday life, making devices more intelligent, responsive, and efficient than ever before.
Conclusion
So guys, in this article, we’ve covered real-life examples of embedded computers in detail. These smart systems are everywhere, working silently to improve our daily lives. It’s remarkable how technology keeps evolving to make our lives more seamless.
Personally, I love how fitness trackers use embedded computers to help monitor health—it’s a small device with a big impact! What devices in your home do you think use embedded computers? Comment below!
FAQs
Here are the most common FAQs about embedded computers to help you understand their functions, importance, and real-world applications.
A regular computer, like a laptop or desktop, can perform many tasks and run different software. An embedded computer is built into a device for a specific function, like controlling a microwave or a car’s braking system. It works automatically and isn’t meant for general use like a PC.
Embedded computers make everyday devices smarter, faster, and more efficient. They automate tasks, improve safety, and help save energy. Without them, modern technology like smart appliances and medical devices wouldn’t function properly.
Most embedded computers have fixed hardware and software designed for a single purpose, so they can’t be upgraded like regular computers. However, some can receive software updates to improve performance. If major changes are needed, the entire unit is often replaced.
Smartphones and mobile phones have embedded systems inside them, but they are not purely embedded computers. Unlike a microwave or smartwatch that performs a single task, these devices can run multiple applications like a regular computer. However, they still rely on embedded components for specific functions like touchscreen control and power management.
Many industries rely on embedded computers, including automotive, healthcare, consumer electronics, industrial automation, and security. They help control cars, run medical devices like pacemakers, power smart home gadgets, and even manage factory robots. Almost every modern industry depends on them in some way.
Not always! Some embedded computers work completely offline, like an airbag system in a car. Others, like smart home devices and GPS systems, use the internet to update data and improve functionality.
It depends on the device! Basic embedded systems, like those in microwaves or washing machines, are low-cost. Advanced ones, like those in medical equipment or self-driving cars, can be very expensive due to their complex functions.
Most embedded computers are protected because they run a single, fixed program that hackers can’t easily access. However, smart devices connected to the internet, like smart TVs or security cameras, can be hacked if they don’t have proper security updates.
Here is a list of common embedded computers at home that you use daily without even realizing it:
- Smart TVs
- TV Remote Control
- Washing Machines
- Microwaves
- Air Conditioners
- Smartwatches
- Refrigerators
- Dishwashers
- Coffee Makers
- Doorbell Cameras
- Smart Thermostats
- Electric Toothbrushes
These devices use embedded computers to automate tasks and enhance efficiency.
Embedded computers automate many tasks, but they don’t replace all jobs. Instead, they help people work more efficiently, like in factories where robots assist workers. Humans are still needed to design, maintain, and improve these systems!

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks